As creators, keeping your creations safe is as important as creating fresh and engaging content for your audience, and understanding the differences between theft and copyright infringement lays the foundation for effective protection.
Both offenses involve the unauthorized use or acquisition of intellectual property, yet they follow distinct legal paths and carry unique consequences.
This article explores the distinctions between these two concepts, with a focus on prevention, legal repercussions, and the proactive measures necessary to secure digital creations.
- Theft, in the context of intellectual property, involves the unauthorized taking or use of someone else’s work intending to deprive the owner of its benefits.
- Copyright infringement often involves civil law, while theft involves property and criminal laws.
- Using watermarks, secure platforms, and transparent copyright policies can help prevent unauthorized access in the digital domain.
Table of Contents
Copyright Infringement vs Theft: What Are the Differences?
Understanding the difference between theft and copyright infringement is essential for creators protecting their works in the digital world.
While both involve the unauthorized use of intellectual property, theft typically refers to the unlawful taking of physical or digital possessions, aiming to deprive the owner of their benefits.
In contrast, copyright infringement revolves around the unauthorized use, reproduction, or distribution of someone else’s copyrighted work, with a focus on creative content such as text, images, music, or videos.
Now, let’s delve into a detailed comparison with the help of the table below:
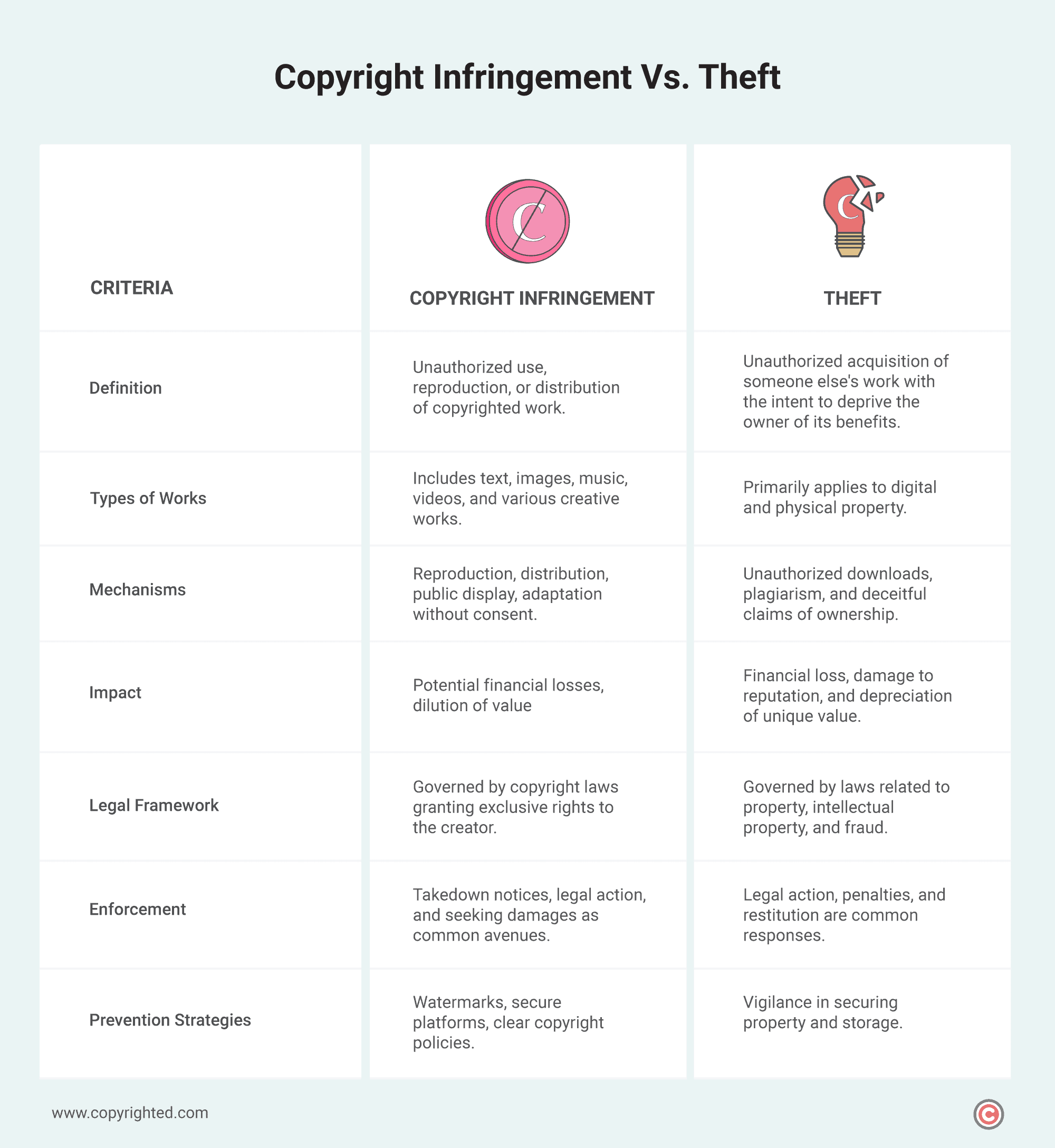
This table provides a snapshot of the key distinctions between copyright infringement and theft, offering a quick reference for your understanding.
Now, let’s provide examples to illustrate the differences.
Imagine someone taking a photographer’s digital image and using it on their website without obtaining permission. This constitutes copyright infringement as it involves the unauthorized use of the photographer’s copyrighted work (the digital image) without proper licensing or consent.
In a separate scenario, consider a situation where a hacker gains unauthorized access to a digital file containing proprietary software code.
he act of taking this digital property without permission would be considered theft in the context of intellectual property, as it involves the unlawful acquisition of valuable digital assets.
These examples aim to highlight the distinctions – the first illustrating copyright infringement through the use of protected content, and the second showcasing theft involving the unauthorized acquisition of digital property.
Now, let’s delve into each aspect to gain a deeper insight into these concepts.
What is Copyright Infringement?
Copyright infringement is the unauthorized use, reproduction, or distribution of someone else’s copyrighted work.
In more detailed terms, it involves a broad spectrum of creative assets, ranging from written content and visual images to musical compositions and video productions.
As creators dedicated to our craft, we invest significant time and passion into developing unique and original content, and unauthorized use can feel like a breach of trust.
Now, let’s dissect the mechanisms of infringement.
Copyright infringement can occur through reproduction, distribution, public display, or even adaptation of an original work without consent from the copyright holder. The impact? Well, beyond potential financial losses, it can dilute the value of a creative work.
Imagine someone using your content without permission – not a pleasant thought, right?
In essence, copyright infringement is not just about legal rights and financial repercussions; it’s about preserving the integrity of artistic expression and maintaining the trust established within the creative community.
It’s a call for creators to ensure that their work is respected and utilized responsibly within the digital landscape. Many educational institutions and professionals actively seek to understand how to avoid plagiarism and copyright infringement to foster ethical practices and protect intellectual property rights.
What is Theft?
Theft, in the context of intellectual property, involves the unauthorized acquisition of someone else’s work with the intent to deprive the owner of its rightful benefits.
Traditionally associated with physical property, in the digital age, theft manifests through several characteristics, including unauthorized downloads, plagiarism, and deceptive claims of ownership.
Unauthorized downloads involve the acquisition of digital content without the creator’s consent. Plagiarism, on the other hand, entails the replication of creative works without proper attribution or authorization.
Additionally, deceitful claims of ownership involve individuals falsely asserting ownership over creative works that are not their own. This overlap between copyright and plagiarism is where ethical and legal considerations often converge.
The consequences of theft closely mirror those of copyright infringement. The aftermath includes not only financial losses but also significant damage to your reputation as a creator.
How is the Legal Framework and Enforcement Structured for Both Cases?
Now, let’s take a closer look at the legal aspects of these matters. The legal framework set up to address copyright infringement and theft is like a protective shield for creators like yourself.
Copyright laws give you special rights over your work, and breaking these rules can lead to legal consequences.
For Copyright Infringement
When it comes to enforcing these laws, there are various methods in play. One common approach is sending out takedown notices.
When a copyright owner discovers unauthorized use of their work, they can send a takedown notice to the party responsible, whether it’s an individual or an online platform. This notice serves as a formal request to remove the infringing content promptly.
However, if the issue persists despite the takedown notice, legal action becomes a more compelling recourse.
This involves taking the matter to court. The copyright owner can file a lawsuit against the infringing party, seeking legal remedies and resolution.
Courts may issue injunctions, ordering the removal of the infringing content, and can also rule on the payment of damages to compensate for the harm caused.
Speaking of damages, if a court determines that the infringement has resulted in financial or reputational harm to the copyright owner, they may award damages to compensate for these losses.
The amount of damages can vary based on factors such as the extent of the infringement, the financial impact on the copyright owner, and any profits gained by the infringing party.
The main goal here is to rectify the infringement, halt unauthorized use, and provide compensation for any adverse effects suffered by the copyright owner.
For Theft
In cases of theft, which traditionally involves the unlawful taking of physical property, the legal framework typically revolves around property and criminal laws rather than copyright statutes.
Enforcing laws against theft often engages law enforcement agencies and the criminal justice system. Unlike copyright infringement, which primarily falls under civil law, theft can result in criminal charges, depending on the severity of the offense.
Criminal consequences may include fines, probation, or imprisonment, reflecting the gravity of the act.
In my view, while going the legal route is a powerful tool, it’s just one piece of the puzzle. Prevention is equally, if not more, important. Think of it like locking your front door to avoid burglars. Similarly, protecting your content involves proactive measures.
You can use watermarks, kind of like a signature on your work, to show it’s yours. Choosing secure platforms for sharing your creations adds an extra layer of protection.
Additionally, being crystal clear about your copyright policies sets expectations for how your work can and cannot be used.
In essence, while the law is there to support you, taking steps upfront to guard your creative endeavors can go a long way in maintaining a secure and respectful digital space for your work.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if you get caught with copyright infringement?
If caught, consequences can include legal action, takedown notices, and potential compensation for damages.
Is copyright infringement a felony or misdemeanor?
It can be either, depending on the severity. Serious cases may lead to criminal charges, making it a felony.
What are 4 examples of copyright infringement?
Examples include unauthorized copying, distribution, public display, and adaptation of copyrighted works without permission.
Is copyright infringement theft?
While not technically theft, it involves unauthorized use of someone else’s work, akin to taking without permission.
Why copyright infringement and plagiarism are like theft?
Both involve the unauthorized use of someone else’s creative work. Copyright infringement and plagiarism deprive creators of the benefits and recognition they deserve for their intellectual efforts, much like traditional theft does with physical property.


