Have you ever discovered your hard work being used online without your permission? It’s frustrating and unfair, yet it happens often in today’s digital age.
Content creators, such as bloggers, artists, musicians, or developers, frequently face the risk of their intellectual property being stolen or misused.
This is where the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) becomes important. The DMCA provides a framework to help creators protect their work from unauthorized use and gives them the tools to take action against copyright infringement.
The article below explains DMCA protection, how it works, and why it’s a necessary resource for anyone publishing content online. By the end, you’ll know how to secure your creations and enforce your rights effectively.
- The DMCA provides a structured legal framework that empowers content creators to protect their intellectual property and address copyright violations online effectively.
- Platforms like YouTube and Facebook implement DMCA provisions such as takedown notices and safe harbor compliance to manage user-generated content and reduce liability.
- Proactive strategies like registering copyrights, using watermarks, and monitoring online content enhance the protection and enforcement of DMCA rights.
Table of Contents
What is the DMCA?
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) is a U.S. law enacted in 1998 to address the growing challenges of copyright protection in the digital media era.
Signed by President Bill Clinton, it represents a major update to copyright law, building on the foundation of the Copyright Act of 1976.
In the late 1990s, digital technology and the internet revolutionized how content was shared and accessed. While this innovation fueled creativity and collaboration, it also led to rampant copyright infringement.
The DMCA was introduced to balance promoting digital progress with protecting creators’ rights. It also incorporated two World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) treaties signed by the U.S. in 1996, aligning national laws with global copyright standards.
The DMCA’s primary goal is to protect copyrighted materials in the digital space. It achieves this by:
- Empowering copyright holders: Through takedown notices, copyright owners can request the removal of unauthorized content from online platforms.
- Establishing safe harbor protections: 17 U.S. Code § 512 shields online service providers, like YouTube and Facebook, from liability for user-generated infringement, provided they comply with specific requirements, such as promptly removing infringing content when notified.
- Prohibiting circumvention of digital protections: Title I of the DMCA makes it illegal to bypass tools like encryption designed to prevent unauthorized access to copyrighted works.
What Does “DMCA Protected” Mean?
When you see “DMCA Protected,” it means that the content or platform adheres to the Digital Millennium Copyright Act guidelines.
This designation ensures that the copyright holder’s rights are safeguarded while providing a structured way to address DMCA violations legally and efficiently.
DMCA protection applies to various content, including text, images, videos, music, and software. Here’s how it works:
- Takedown Notices: If someone uses your content without permission, you can file formal DMCA takedowns to request the removal of the infringing material.
- Safe Harbor Compliance: Platforms like YouTube, Facebook, and WordPress implement DMCA protections to limit their liability for user-generated content.
- Anti-Piracy Measures: Streaming services such as Netflix and Amazon utilize encryption and other technologies to prevent unauthorized copying and downloads, in line with 17 U.S. Code § 1201.
Platforms across various industries implement DMCA protections to uphold copyright laws and address infringement effectively.
For instance, YouTube uses tools like Content ID and takedown procedures to manage copyright claims, while Facebook provides reporting mechanisms that allow creators to flag unauthorized use of their content.
E-commerce platforms like Etsy and eBay enable copyright owners to report listings violating intellectual property rights. Additionally, web hosting providers like Bluehost and GoDaddy comply with DMCA notices by removing infringing material from their servers.
How Does DMCA Protection Work?
DMCA protection provides a structured approach for creators to safeguard their work and address copyright violations. It can be utilized proactively by registering your work or reactively by issuing a takedown notice when infringement occurs.
Registering Your Work for DMCA Protection
While registration isn’t required to benefit from DMCA protections, it strengthens your legal position if disputes arise.
To register your work with the U.S. Copyright Office, you must:
- Submit Your Work: Complete the application process for your work type (e.g., literary, visual, or audio) on the U.S. Copyright Office website.
- Provide Supporting Materials: Upload or mail a copy of your work for review.
- Pay the Registration Fee: Fees vary depending on submission type (online or physical).
- Receive Certification: Once approved, your work is registered, simplifying enforcement in legal actions.
Issuing a DMCA Takedown Notice
If you find your intellectual property being used without authorization, the DMCA offers a straightforward process for your work’s security:
- Identify the Infringement: Document the unauthorized use by taking screenshots or saving copies as evidence.
- Prepare Your Notice: Include the following details:
- Your name and contact information.
- A description of the copyrighted work.
- The URL or location of the infringing content.
- A statement asserting your belief that the use is unauthorized.
- A sworn declaration that your notice is accurate.
- Submit the Notice: Send it to the designated agent of the infringing platform or hosting provider, following their specified DMCA complaint process.
- Await Action: Upon receipt, platforms typically promptly remove infringing content to maintain their safe harbor status.
After the Takedown Notice
Once processed, the infringer may file a counter-notice if they believe the content was removed in error. In such cases, you may need to pursue further legal action to resolve the matter.
How to Ensure Your Content is DMCA Protected?
Ensuring your content is DMCA-protected involves proactive and reactive strategies to safeguard your intellectual property. While DMCA protections automatically apply to original works, taking additional steps can enhance your ability to enforce those rights effectively.
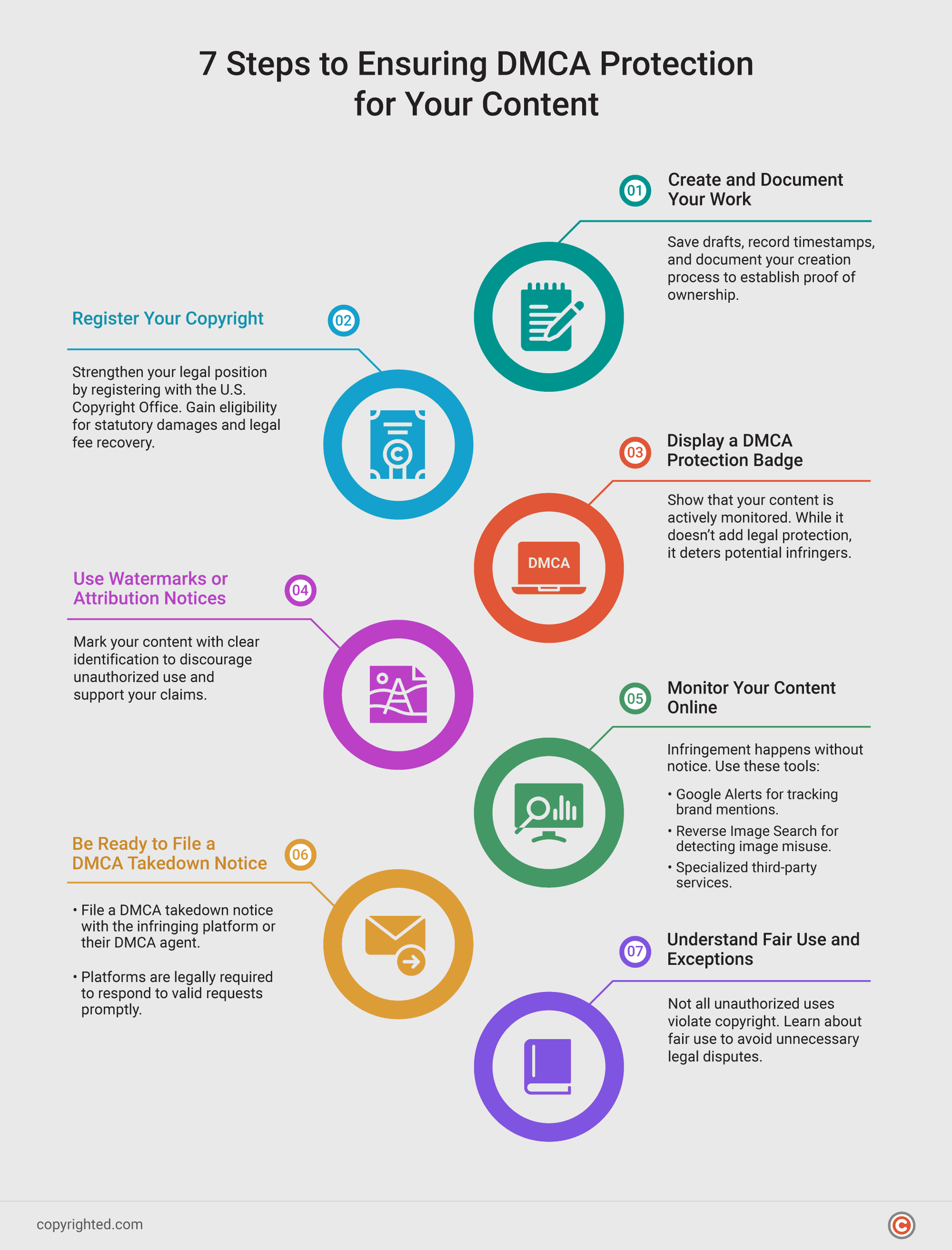
1. Create and Document Your Work
DMCA protections cover original works of authorship, including text, images, music, videos, and software.
To establish proof of ownership, creators should save drafts and revisions, record timestamps using secure cloud storage or similar tools, and maintain detailed records of the creation process.
2. Register Your Copyright
While DMCA protection does not require registration, registering your work with the U.S. Copyright Office significantly strengthens your legal position.
It provides official proof of ownership, which is essential for resolving disputes and makes you eligible to claim statutory damages and legal fees if you file a lawsuit under 17 U.S.C. § 504.
3. Display a DMCA Protection Badge
Adding a DMCA badge to your website signals that your content is actively monitored under the DMCA. While a badge doesn’t enhance legal protections, it may deter potential infringers.
4. Use Watermarks or Attribution Notices
For visual or written content, include watermarks or attribution to identify yourself as the creator clearly. These technological protection measures discourage unauthorized use and support your claims in case of disputes.
5. Monitor Your Content Online
Digital copyright infringement can occur without your knowledge. Use these tools to stay vigilant:
- Google Alerts: Track mentions of your content or brand.
- Reverse Image Search: Detect misuse of images.
- Third-Party Services: Many platforms offer specialized monitoring solutions.
6. Be Ready to File a DMCA Takedown Notice
If you come across infringement, get ready to file a DMCA takedown notice. Send your notice to the infringing platform or their designated DMCA agent for action.
By law, platforms must respond quickly to valid takedown requests, protecting your content.
7. Understand Fair Use and Exceptions
Not all unauthorized uses violate the DMCA copyright law.
For instance, 17 U.S. Code § 107 defines fair use, which includes purposes like commentary, criticism, and education. Familiarize yourself with these exceptions before pursuing legal action.
Frequently Asked Questions
What kinds of digital content are DMCA-protected?
Content such as music, videos, images, eBooks, software, and online articles are all eligible for DMCA protection.
Does DMCA protection cover all types of copyright infringement?
DMCA protection is designed to address online copyright infringement but does not apply to offline or physical-world copyright violations.
Do you need to register your work to get DMCA protection?
While registration is not mandatory, registering your copyright makes enforcement under the DMCA easier and more effective.
Can DMCA protections be abused?
Yes, some individuals or companies misuse takedown notices to target legitimate uses like fair use or competitors.
What happens if a website ignores a DMCA takedown notice?
If a website ignores a valid DMCA takedown notice, it risks losing its safe harbor protection and may face legal consequences for hosting infringing content.


